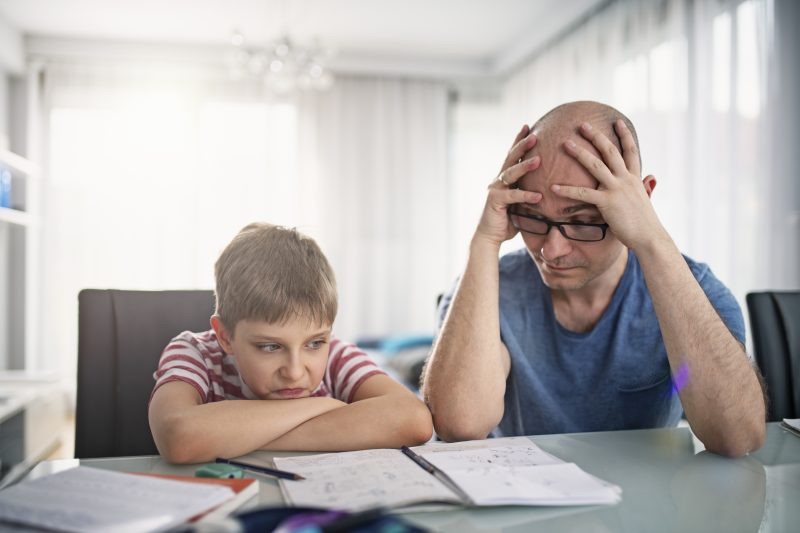
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is characterized by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. People with ADHD may struggle with maintaining focus, organizing tasks and activities, following through on instructions, and regulating their behavior and emotions. This can impact their academic, social, and occupational functioning and may call for treatments such as medication, therapy, and behavioral interventions.
ADHD symptoms usually become apparent at a young age, and more noticeable as a child’s circumstances change, like when they begin school. More often than not, ADHD is diagnosed when the person is between 6 and 12 years old. While the symptoms improve with age, most adults who were diagnosed with ADHD at a young age still experience certain issues.
Table of Contents
Seeking Help
Almost every child undergoes a stage where they are inattentive and restless. This is normal and does not necessarily mean they suffer from ADHD. However, if you think your young one’s behavior is significantly different from others in their age, it is best to raise your concerns with the teacher, the school’s special educational needs coordinator, or the General Practitioner (GP) for an ADHD assessment Edinburgh.
You may also want to consult your doctor if you are an adult portraying ADHD symptoms but were not diagnosed with the condition when young.
What Causes ADHD?
The primary cause of this condition is not fully understood, but it has been observed to have a genetic component that runs in the family. Studies have also identified various differences in the brain structures of individuals with ADHD compared to those without the disorder.
There are other factors that have been proposed to play a potential role in the development of ADHD, including:
-Premature birth (usually before the 37th week of pregnancy)
-Low birth weight
-Alcohol consumption, drug use, or smoking while pregnant.
ADHD is shown to be more common in boys and about 2 to 5 percent of school-aged kids may have the condition. And while it is more common in individuals with learning difficulties, people of any intellectual capacity can get the disorder.
How is ADHD Treated?
While there is no known cure for ADHD, it can be effectively managed with appropriate educational support, guidance for parents and affected individuals, and in some cases, medication.
In regards to treating adults with ADHD, medication is often the initial approach, although psychological therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) may also be beneficial.
Leading Life with ADHD
Taking care of a child with ADHD can present various challenges, but it is crucial to keep in mind that the young one cannot control their behavior. Examples of day-to-day challenges that may arise include:
-Getting the child to bed at night
-Having them ready for school on time
-Staying organized
-Paying attention and following instructions
-Social occasions
Adults struggling with the disorder may also encounter similar issues, in addition to problems with employment, drug use, and crime.